Tips, Good Practices and Errors¶
Tips¶
- Use job priority
Job priority is a new feature in version 2.1. The jobs have a new integer attribute named priority (see Workflow creation API).
low_priority_job = Job(command=["program", "argument"], name="job 1", priority=0) high_priority_job = Job(command=["program", "argument"], name="job 2", priority=10)
The priority is set to 0 by default. Its value is used by Soma-workflow to sort the jobs which are ready to be submitted. As a consequence, the jobs with higher priority are submitted first. Note that the dependencies between jobs defined in the workflow are always satisfied.
Job priorities can be used, for example, to obtain intermediate results more quickly in a workflow:
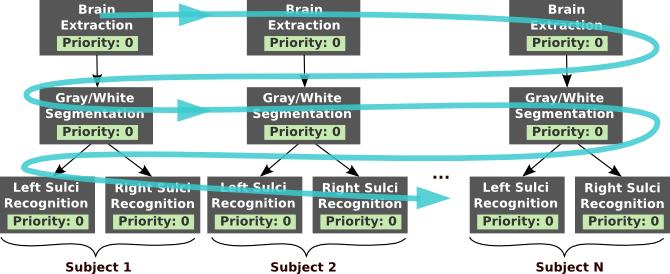
Without job priority: depending on the number of cpu available the tendency will be to execute all the “brain extraction” jobs, then all the “gray/white segmentation” jobs and so on. As a consequence, the result of the whole processing of the first subject will be available late in the workflow execution.¶
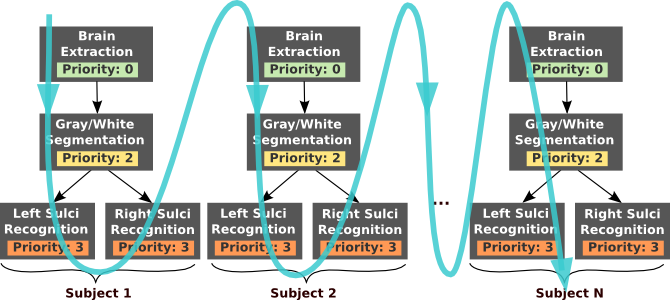
With job priorities: the “sulci recognition” jobs have higher priority. Depending of the number of cpu available, the “sulci recognition” jobs will tend to be executed before all the “brain extraction” and “gray/white segmentation” jobs end. As a consequence, the result of the whole processing of the subject 1 will be available early in the workflow execution.¶
- Use native specification to access the full range of features of your cluster
Some specific option/feature of your cluster might not be usable through the unified interface of Soma-workflow. The native specification string makes them available.
For example, the native specification parameter can be used to specify the walltime of a job:
#Using a PBS cluster: job = Job(command=["program", "argument"], name="max one hour job", native_specification="-l walltime=01:00:00")
#Using a SGE cluster: job = Job(command=["program", "argument"], name="max one hour job", native_specification="-l h_rt=01:00:00")
The main problem of native specification is that it makes jobs dependent of the resource which will be used for the execution (in the previous example the job created for the PBS cluster can not be used on the SGE cluster). To avoid this drawback, a default native configuration string can be configured for each resource and will be applied to every job submitted to the resource (see Configuration items optional on the server side:).
- Avoid some typing
A login and password are required when you connect to a remote computing resource.
Configure an ssh authentication by RSA key to avoid typing your password in the GUI or worse, in a Python script.
Configure a login for each remote computing resource in the configuration file of Soma-workflow (LOGIN configuration variable). The configured login will be used to prefill the GUI.
Good Practices on a cluster¶
- Do not forget that computing resources have usually their own rules and are shared with other users
Everything you do through Soma-workflow is done with your user id on the computing resource.
- Choose an appropriate queue to run your workflows depending on the job size.
See Configuration (Created automatically) to configure the queues so that they will appear in the GUI.
- Use the queue limitation feature.
Because workflows can contain a lot of jobs, it is very useful to limit the number of jobs which can be waiting in the queue at the same time. The are three main reasons to do so:
It is a good practice not to saturate the queue with too many jobs. If you set up a limit and submit a workflow, the other users will be able to intercalate their own jobs. Since they will not have to wait for you 500 jobs (or more) in the queue to see their own jobs running, you will not receive angry phone calls.
On some computing resources, the limit is configured in the DRMS. If you try to submit a job while you already reached the limit it will produce an error.
If you use the job priority feature, the effect of the priority you set will be more visible if a limitation is configured for the queue. Indeed, once submitted to the cluster the jobs can not be sorted anymore by priority.
When a limit is set up, the jobs which are ready to be submitted but are waiting because the limit is reached have the status “pending” (see Status list). They are actually waiting in a queue internal to soma-workflow in which the jobs are sorted by priority.
See Configuration items optional on the server side: to set up the limitation.
Note
The limitation of the number of job in a queue does not limit the number of job which can run in parallel. However, because the other users can intercalate their own jobs and because of the system delay, it can take more time to get all the jobs running.
- One database per user.
The soma-workflow will start one database when the user connects to the server.
Good Practices in general¶
- Do not build workflows with too many short jobs.
Depending on the system the time for the jobs to be submitted is variable and is usually not instantaneous. To take advantage of running your workflow in parallel, the jobs should not be too short: more than 1 minute usually.
- Open only one application at a time in the mono process mode.
This will be fixed in a future version. It includes the use of Soma-workflow on a multiple core machine.
Errors¶
Here is the list of the various errors which can occur when using Soma-workflow.
- class errors.ConfigurationError(Exception)[source]¶
Raised when the configuration is not correct or when configuration items are missing.
- class errors.ConnectionError(Exception)[source]¶
Raised when the connection could not be set up with the computing resource and/or the database server.
- class errors.JobError(Exception)[source]¶
Raised when an incorrect Job is submitted to soma-workflow.
- class errors.WorkflowError(Exception)[source]¶
Raised when an incorrect Workflow is submitted to soma-workflow.
- class errors.TransferError(Exception)[source]¶
Raised when an incorrect Transfer is submitted to soma_workflow, or when an error occurs during a file transfer.
- class errors.UnknownObjectError(Exception)[source]¶
Raised when an operation is attempted on Jobs, Workflows or Transfers which do not exist or do not belong to the user.
