User documentation¶
Installation¶
From PyPI:
# A compatible version of Python and Pip must be installed
To install pip:
sudo apt-get install python-pip # Python2
sudo apt-get install python3-pip # Python3
# To install the module:
sudo pip install populse-db # Beware that it is the Pip version corresponding to the good Python version
sudo pipx.x install populse-db # With a precise Pip version
sudo pythonx.x -m pip install populse-db # With a precise Python version
From source:
# A compatible version of Python must be installed
sudo apt-get install git
git clone https://github.com/populse/populse_db.git /tmp/populse_db
cd /tmp/populse_db
sudo python setup.py install # Beware that it is the good Python version (use pythonx.x to be sure)
cd /tmp
sudo rm -r /tmp/populse_db
Usage¶
Import examples:
import populse_db
from populse_db.database import Database
import populse_db.database
Tests¶
Unit tests have been written with the package unittest
Continuous integration has been deployed with Travis (Linux, OSX), and AppVeyor (Windows)
The code coverage is generated with the package codecov
The script of tests is python/populse_db/test.py, so the following command launches the tests:
python test.py # (if python/populse_db/ directory has been added to $PATH, or if $PWD in the terminal)
python python/populse_db/test.py # (from populse_db root directory)
python -m populse_db.test
Using populse_db¶
Small script to show the initialization and some examples of calls:
import os
import tempfile
import shutil
from populse_db.database import Database, FIELD_TYPE_STRING, FIELD_TYPE_INTEGER
# Generating the database in a temp directory
temp_folder = tempfile.mkdtemp()
path = os.path.join(temp_folder, "test.db")
database_url = 'sqlite:///' + path
database = Database(database_url)
# Creating the session and working with it
with database as session:
# Creating a profile table
session.add_collection("Profile")
# Adding several properties
session.add_field("Profile", "First name", FIELD_TYPE_STRING)
session.add_field("Profile", "Last name", FIELD_TYPE_STRING)
session.add_field("Profile", "Age", FIELD_TYPE_INTEGER)
# Filling the table
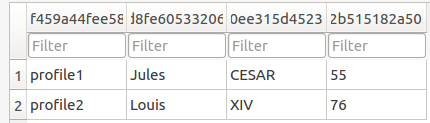
profile1 = {}
profile1["index"] = "profile1"
profile1["First name"] = "Jules"
profile1["Last name"] = "CESAR"
profile1["Age"] = 55
session.add_document("Profile", profile1)
session.add_document("Profile", "profile2")
session.add_value("Profile", "profile2", "First name", "Louis")
session.add_value("Profile", "profile2", "Last name", "XIV")
session.add_value("Profile", "profile2", "Age", 76)
# Setting a value
result = session.filter_documents("Profile", "({Age} > 50) AND ({First name} == \"Jules\")")
for document in result: # profile1 is displayed, as it's the only document with the value Age greater than 50, and the value First name being Jules
print(document.index)
shutil.rmtree(temp_folder)
The database file test.py resulting from the script is available here.
As you can see in the collection table, the collection Profile has been created.
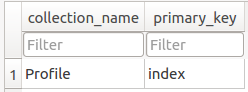
As you can see in the field table, the three fields First name, Last name, and Age have been created, in addition to the primary key.
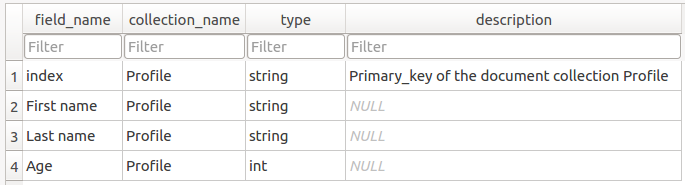
As you can see in the collection profile table, the two profiles Jules CESAR and Louis XIV have been created.